Ground Anchor Drilling Method for Landslide Prevention
Under the impact of severe climate change, the increasing frequency of slope failures has become a serious risk to both infrastructure and human safety. An effective countermeasure is the use of ground anchor drilling to firmly stabilize deep slip surfaces and prevent soil erosion.
What is Ground Anchor Drilling?
A ground anchor system is designed to provide stability and resist excessive displacement of retaining structures by applying prestressed forces into the soil and rock. Ground anchor drilling is commonly associated with civil infrastructure projects that require high precision in design standards and installation.
Ground anchors address stability challenges across various scales and geotechnical environments. Engineers have adopted ground anchor drilling in civil infrastructure projects that demand high precision in both design and installation standards. Anchors eliminate the need for excavation behind retaining walls and allow for top-down construction, reducing the amount of temporary support required.
What Are the Types of Ground Anchor Drilling?
To meet usage demands, anchors are classified into three types: temporary anchors, permanent anchors, and ground anchors. Each type has its own function and characteristics suited to different applications:
a. Removable ground anchors:
This is a temporary ground anchor product designed to stabilize diaphragm or sheet pile walls of excavation pits. It can be removed, allowing the prestressing cable to be retrieved after use.
In addition to its environmental benefits, at construction sites with deep excavations in urban areas, avoiding leftover underground obstructions is essential, as these can pose challenges for nearby future construction projects.
The SSC-RA removable ground anchor system effectively addresses this issue. Once the basement floors are completed and pressure inside and outside the retaining wall is balanced, the entire prestressing cable embedded underground is fully retrieved. Consequently, there is no longer concern about encountering buried tendons during the construction of adjacent bored piles or retaining walls.
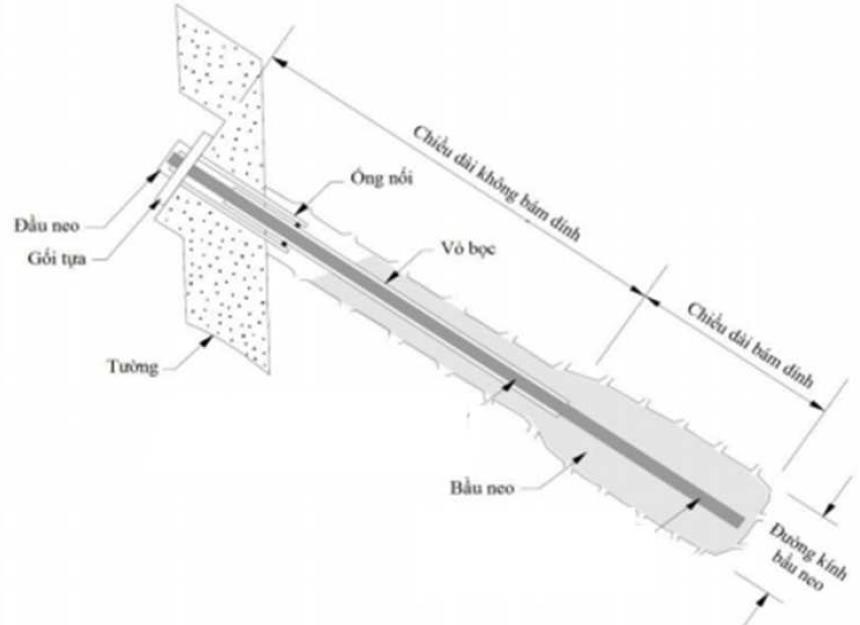
b. Temporary Ground Anchors:
As a temporary solution, this type of anchor is designed for use within a period of less than two years. Once installed, it cannot be removed. It is primarily applied in deep excavation works with diaphragm walls or sheet pile walls. Despite being labeled “temporary,” it plays a crucial role during construction by enhancing stability, accelerating the construction schedule, and offering flexibility in application.
Thanks to its use, the basement area gains additional space for construction activities. However, a notable limitation is the difficulty in execution near adjacent structures. Temporary ground anchors transfer tensile force through contact points in the soil or rock mass. One end is anchored in the soil to generate frictional resistance, while the other end is connected to the retaining structure. This type is commonly used for dismantling structures such as diaphragm walls, bored pile walls, sheet pile walls, and is frequently applied across various types of construction projects.

c. Permanent Ground Anchors:
This type of ground anchor is designed for long-term use and serves the purpose of stabilizing permanent retaining structures and slopes. It is fixed into the ground to generate frictional resistance and counteract uplift forces, including foundation buoyancy and pullout forces, thanks to highly effective anti-oxidation and corrosion-resistant protective layers.
In particular, its corrosion resistance is further enhanced by a plastic end cap attached to the anchor head. Transportation and installation are made simple due to its packaging in coiled form, allowing for easy handling and storage. Depending on the installation depth, the length of the tendons and spiral sleeves can be adjusted accordingly. With these superior features, permanent ground anchors are widely used in slope stabilization, retaining walls, foundations for hydraulic and transportation infrastructure projects around the world.
Applications of Ground Anchors:
In construction projects, ground anchors are a reliable solution to ensure stability and a fixed support system. Below are some key applications frequently utilized:
- Anchoring retaining walls during excavation works at construction sites.
- Stabilizing slopes.
- Resisting uplift pressure from groundwater on structures.
- Stabilizing and enhancing the performance of tunnels.
- Stabilizing structures against seismic forces.
- Stabilizing tower-like structures such as power poles and broadcasting towers.
- Stabilizing bridge pier foundations.
Some useful information related to ground anchors:
- Cable strands are fixed to anchor heads and tensioning devices.
- Ground anchors are embedded into the soil.
- The anchor head is grouted with cement to bond it firmly to the ground.
- Lateral pressures are significantly reduced, thereby stabilizing retaining walls.
- The anchor body consists of multiple elastic cable strands.
Depending on actual site conditions, drilling angles and tension forces relate directly to the anchoring force.
Ground anchor technology for landslide prevention is widely applied on many slopes and retaining walls in construction projects.
Carrying the mission of “Trust for every structure,” Minh Duc Group, supported by leading engineers in the field, has continuously innovated and improved construction quality. The Group has earned long-term satisfaction and cooperation from numerous investors and project owners. Learn more about landslide-prevention ground anchors through articles on our website.
